Are you thankful when your doctor tells you your cough, sore throat, ear and sinus pain don’t need an antibiotic? You should be. Their side effects go way beyond antibiotic-resistant bacteria—they mess with our microbiome/immune system. The consequences may be far reaching including cancer. See below. Hugo Rodier, MD
Antibiotics Use and Subsequent Risk of Colorectal Cancer
Journal of the National Cancer Institute 2022;114:38–46
“This register-based study covering the entire population of Sweden found a robust association between antibiotics use and higher risk of proximal colon cancer and an inverse association with rectal cancer in women. This study strengthens the evidence from previous investigations and adds important insight into site-specific colorectal carcinogenesis.”
No-meat, low-meat diets may lower risks of common cancers
“HealthDay (2/24, Norton) reports people who adhere to no-meat and low-meat diets “may have lower risks of some of the most common cancers, a…large study suggests.” The study published in BMC Medicine was “based on more than 472,000 U.K. adults” and evaluated the impact of “no-meat and low-meat diets” on risks of colon, breast, and prostate cancers.”
Comment: meat has adverse effects on our gut flora; it triggers more inflammation, which has been identified as one of the factors leading to cancer.
Gut microbial composition and healthy cognitive function
“Healio (2/11, Herpen). “Gut microbial composition was positively associated with healthy cognitive function in middle-aged adults,” investigators concluded in the study Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults cohort, a 30-year follow-up with 3,358 participants, aged 48 to 60 years, from 2015 to 2016.” The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.”
Comment: Inflammation is also involved here, as is suboptimal detoxification. Remember that aluminum is ubiquitous (antiperspirants, cans). It has been associated with cognitive problems. I would rather have wet underarms than a wet brain…
Proton pump inhibitors and risk of gastric cancer
J. Gut Jan 2022
“The findings of this large population-based cohort study indicate that the use of PPIs is associated with an increased risk of gastric cancer compared with the use of Zantac, Pepcid, although the absolute risk remains low.”
Comment: the risk IS low, but when you add it to other factors, like toxins in the environment, genetics and a poor microbiome, it adds up.
Formaldehyde and likelihood of memory, thinking problems
“The Washington Post (2/13, Searing) “Health workers and others who are exposed on the job to formaldehyde, even in low amounts, face a 17% increased likelihood of developing memory and thinking problems later on,” investigators concluded after examining “data from more than 75,000 people. “At highest risk were those whose work had exposed them to formaldehyde for 22 years or more, giving them a 21% higher risk for cognitive problems than those who had not been exposed.” The findings were published in the journal Neurology.”
Comment: Formaldehyde in Your Home: What you need to know | Formaldehyde and Your Health | ATSDR (cdc.gov). If you cannot avoid it, eat a lot of veggies to maximize your detox pathways in the gut and liver.
Aquatic exercise superior to physical therapy in chronic lower back pain
Healio Minute, January 25, 2022
“Therapeutic aquatic exercise results in greater lower back pain relief than physical therapy, and demonstrates long-term effects for up to 12 months, according to data published in JAMA Network Open. “Among the numerous therapeutic exercises available, therapeutic aquatic exercise is often prescribed by physicians for chronic low back pain, and it is becoming increasingly popular for treatment of chronic low back pain,” Meng-Si Peng, MSc, of the Shanghai University of Sport, in China, and colleagues wrote. “Water is an ideal environment for conducting an exercise program given its various properties, including buoyancy pressure, density, thermal capacity and conductivity.”
Comment: Both together are best. Get your rubber ducky out.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of incident chronic kidney disease
J. Gut Jan 2022
“This large and updated meta-analysis indicates that NAFLD is significantly associated with a~1.45-fold increased long-term risk of incident CKD stage ≥3. Further studies are needed to examine the association between the severity of NAFLD and risk of incident CKD.”
Comment: Fatty liver curtails its detox functions. The slack is picked up by the kidneys.
Gut microbiota modulates COPD
J. Gut Jan 2022
“The gut microbiota–lung COPD axis was connected. A potentially beneficial bacterial strain the anti-inflammatory Parabacteroides goldsteinii lipopolysaccharide and its functional component may be developed and used as alternative agents for COPD prevention or treatment.”
Comment: soon we will know what microbiome bacteria is positively/negatively associated with each disease.
Host–Microbiota Interactions in the Esophagus During Homeostasis and Allergic Inflammation
J. Gastroenterology 2022;162:521-534
“The esophagus has a unique microbiome with notable differences between its proximal and distal regions. Fecal matter transplantation restores the esophageal microbiome. Antibiotic-induced dysbiosis exacerbates disease in a murine model of EoE. Collectively, these data establish the composition, transplantation potential, antibiotic responsiveness, and host–microbiota interaction in the esophagus and have implications for gastrointestinal health and disease.”
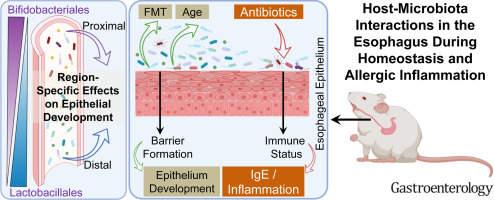
Comment: blaming acid for reflux does not make sense. The problem is inflamed cells lining the esophagus, which makes them more susceptible to acid. Now you know why they are inflamed.
Effect of melatonin supplementation on sleep quality
Journal of Neurology 2022;269:205–216
“The treatment with exogenous melatonin has positive effects on sleep quality as assessed by the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) in adult. In adults with respiratory diseases, metabolic disorders, primary sleep disorders, not with mental disorders, neurodegenerative diseases and other diseases.”
Comment: melatonin is related to serotonin, a calming neurotransmitter we make in the brain if we eat good food rich in B complex, tryptophan and minerals.
Is high dietary quality the real fountain of youth?
The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2022:115:6–7
“DNA methylation is one of the most studied epigenetic marks related to chronic disease risk. Changes in DNA methylation have been implicated in the pathogenesis of diseases that are largely influenced by dietary quality, including cardiovascular disease and cancer. Recent work suggests that diet can have a major impact on an individual’s epigenome. For example, in an epigenome-wide analysis, DNA methylation was correlated with dietary quality measured by both the Mediterranean-style Diet Score (MDS) and the Alternative Healthy Eating Index (AHEI) (1). In this analysis of the causal association between diet quality, changes in DNA methylation, and cardiovascular disease risk, the authors found that dietary quality rather than cardiovascular disease was more likely to contribute to the observed DNA methylation changes. Furthermore, the diet-associated DNA methylation changes were also associated with a higher risk for all-cause mortality.”
Comment: methylation, adding B complex vitamins to proteins, is indeed important. So is the prebiotics function of fiber—it feeds the microbiome.


